9/6/21 warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface by atmospheric gases Solar energy radiating back to space from the Earth's surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases and reemitted in all directions This heats both the lower atmosphere and the surface of the planetFormerly used as a refrigerant and as a propellant in aerosol cans;

Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
What are greenhouse gases simple definition
What are greenhouse gases simple definition-Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewedThe greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com
The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement adopted in 1997 that aimed to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and the presence of greenhouse gasesGreenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortableGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons
Definition of Greenhouse gas A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared rangeThis process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneWe saw the family of past and possible future trajectories of greenhouse gas emissions and concentrations earlier in the course But what are the specific greenhouse gases involved, other than the obvious culprit CO 2, and where are these emissions actually coming from?What are the sectors of society and economy responsible for these emissions, the potential for reducingClimate change refers to significant changes in global temperature, precipitation, wind patterns and other measures of climate that occur over several decades or longer Discover an AZ glossary of concise scientific explanations to help readers better understand climate change from science to
26/7/ Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder on average than it is now Greenhouse gases absorb energyDefine greenhouse gases greenhouse gases synonyms, greenhouse gases pronunciation, greenhouse gases translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozone See greenhouse effectThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples
However, the actual contribution of a greenhouse gas to atmospheric warming depends not only on its GWP, but also on its concentration At present, the concentrations of halogenated gases in the atmosphere are low and their combined radiative forcing is only about onefifth that of CO 2Global warming is mostly because of people burning things, like gasoline to make cars go and natural gas to keep houses warm But the heat from the burning itself only makes the world a tiny bit warmer it is the carbon dioxide from the burning which is the biggest part of the problem Among the greenhouse gases, the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is the main5/3/19 Switching to natural gas is an improvement over coal, but a transition to zeroemission sources of energy and heat (solar, wind, geothermal or nuclear) is needed to fully clean up our energy system Agriculture & Land Roughly onefifth of all global greenhouse gas emissions come from our use of land, mainly from deforestation and emissions




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
30/1/17 Greenhouse gases vary in not only their sources and the measures needed to control them, but also in how intensely they trap solar heat, how long they last once they're in the atmosphere, and how they react with other gases and ultimately get flushed out of the air› en español Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respondGreenhouse gases occur naturally and allow us to survive on Earth by warming air near Earth's surface Human activities are now increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which leads to changes in climate These changes are affecting many human activities, including agriculture GrEENHOUSE GAS BASICS




Nasa S Climate Kids What Is The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Earth Science Homeschool Current Events For Kids



1
Greenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn moreMuch like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it22/6/21 Data can be displayed for individual Parties or groups of Parties, for different greenhouse gases or for their sum, and in varying degrees of detail To find the exact GHG data required, the user is advised to consult the following table where typical user requirements are mapped against the data availability on this site



Lecture 14 Radiative Equilibrium And The Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
25/1/07 A carbon footprint is defined as the total amount of greenhouse gases produced to directly and indirectly support human activities, usually expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) In other words When you drive a car, the engine burns fuel which creates a certain amount of CO2, depending on its fuel consumption and the driving distanceGreenhouse gas Significado, definición, qué es greenhouse gas 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Aprender más13/7/21 Greenhouse definition A greenhouse is a glass building in which you grow plants that need to be protected from Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
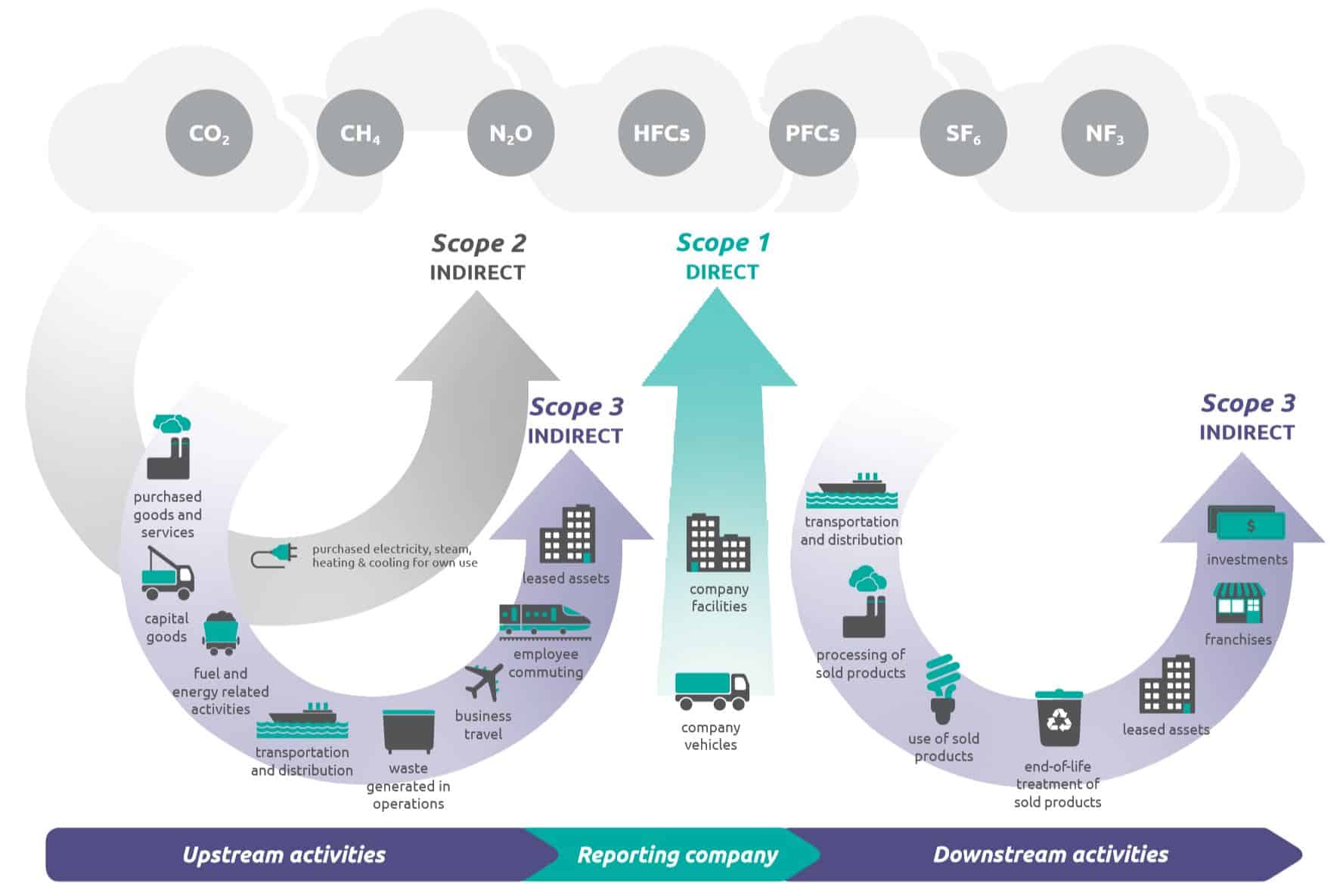



What Is The Difference Between Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Compare Your Footprint
10/5/21 Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;13/5/06 A greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases This is called the " greenhouse effect " Most greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on EarthThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), and methane When there is more greenhouse gas in the air, the air holds more heat This is why more greenhouse gases cause climate change and global warming The greenhouse effect is natural



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
14/7/21 (Extractive engineering General) A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere14/8/ Greenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gasesGreenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences
8/7/16 In simple terms, gases that trap heat in the earth's atmosphere are known as Greenhouse Gases, abbreviated as GHGs They contribute to the Greenhouse Effect, which is the resultant heating effect Greenhouse Effect Explanation A greenhouse or a glasshouse is a closed glass structure in which plants are grown in regulated climatic conditions1/8/01 The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itGreenhouse gas a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation greenhouse emission CFC , chlorofluorocarbon a fluorocarbon with chlorine;
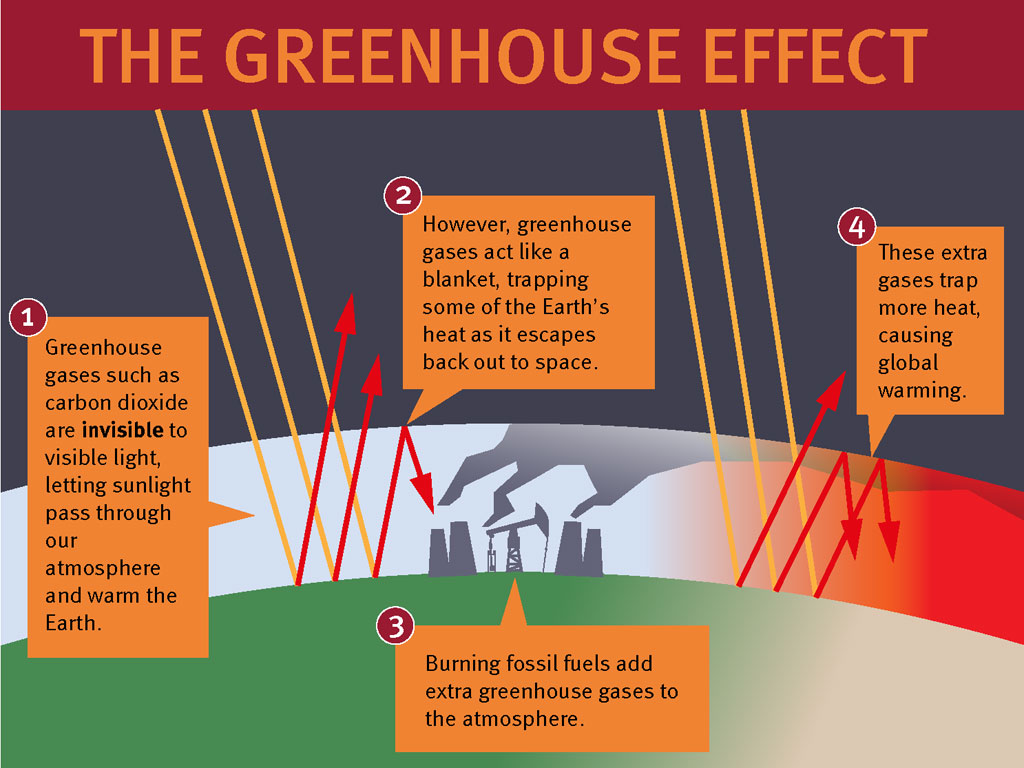



7 1 Old First Wombat On Earth
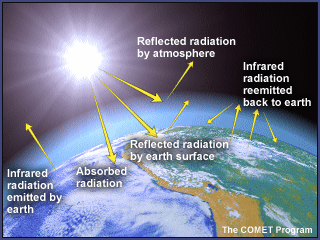



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
Definition of greenhouse gas any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation4/1/ Definition Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effect15/7/21 The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides



Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existDEFINITION An atmospheric gas, such as water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide that absorbs and emits radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surfaceHuman activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests, have led to a rise in greenhouse gas emissions, causing global warming"the chlorine in CFCs causes depletion of atmospheric ozone"




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
A greenhouse gas has a stronger impact on theradiative balance of the Earth if it interacts withlight in the middle of the Earthlight spectrum Band saturation A greenhouse gas at relativelyhigh concentration like CO2will be less effective, molecule per molecule, than a dilute gaslike methane16/7/21 Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




The Global Effects Of Environment Change




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases



1
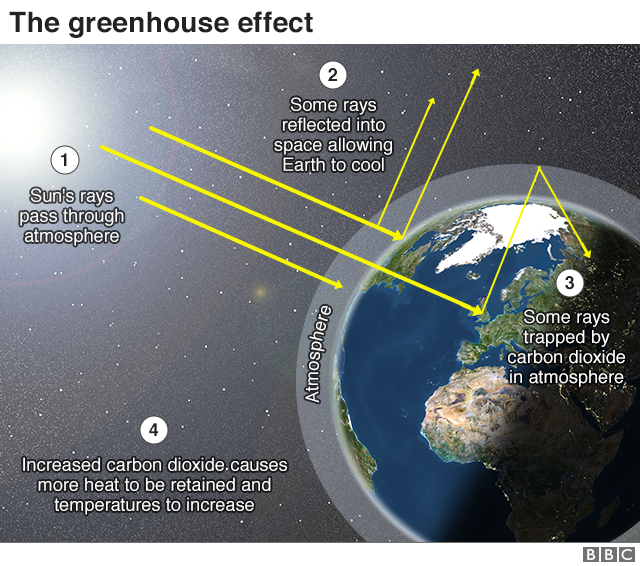



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News



The Greenhouse Effect




10 Solutions For Climate Change Scientific American




Conscious Home Simple Ways To Combat The Effects Of Climate Change At Home Courtesy Of Porch Com




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate
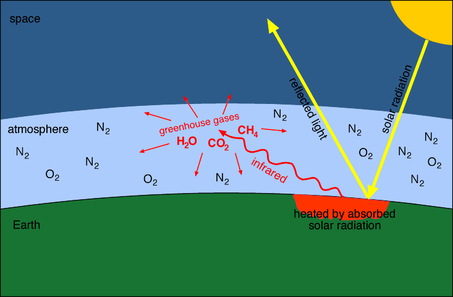



Greenhouse Gases Biology Notes For Igcse 14




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Carbon Dioxide Ucar Center For Science Education
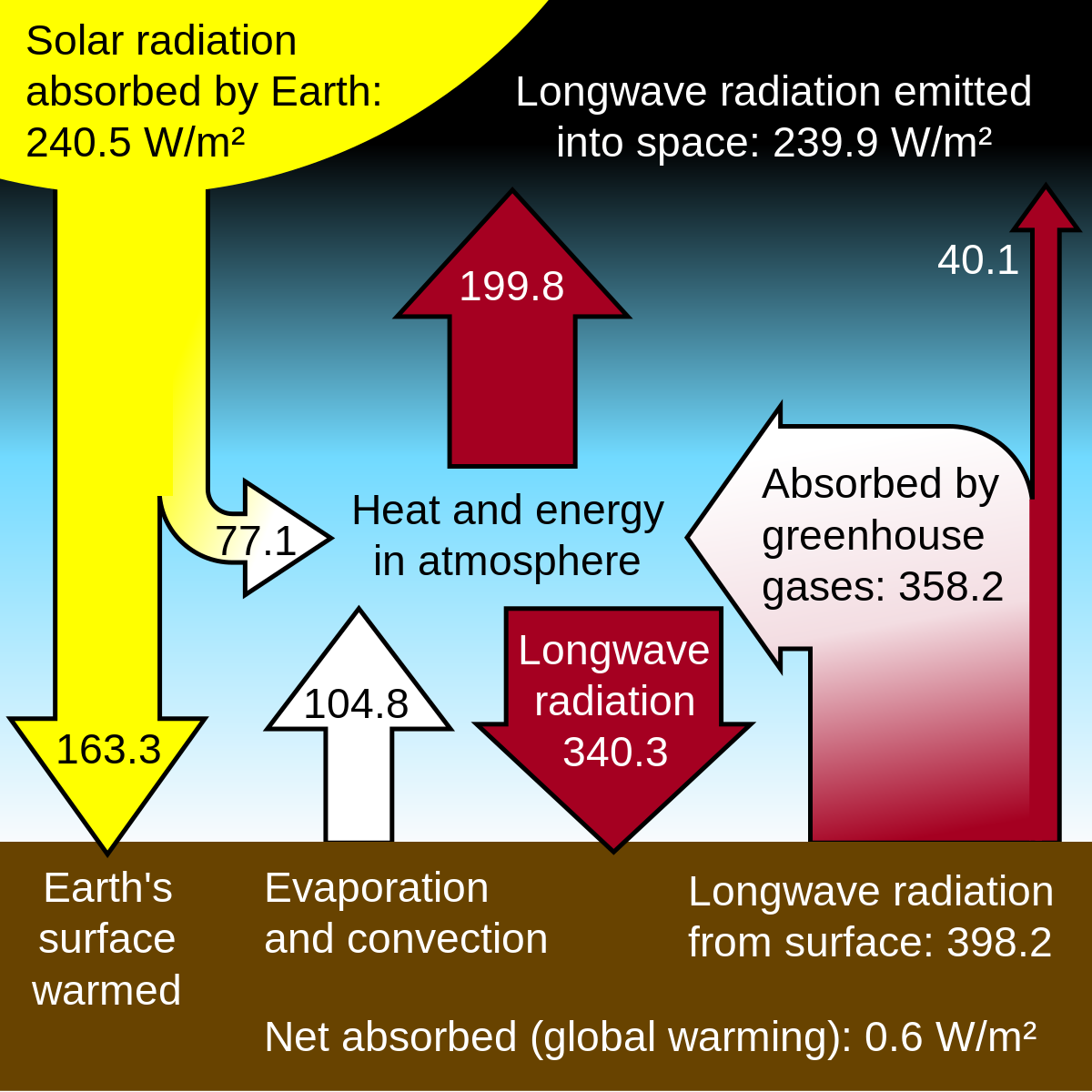



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
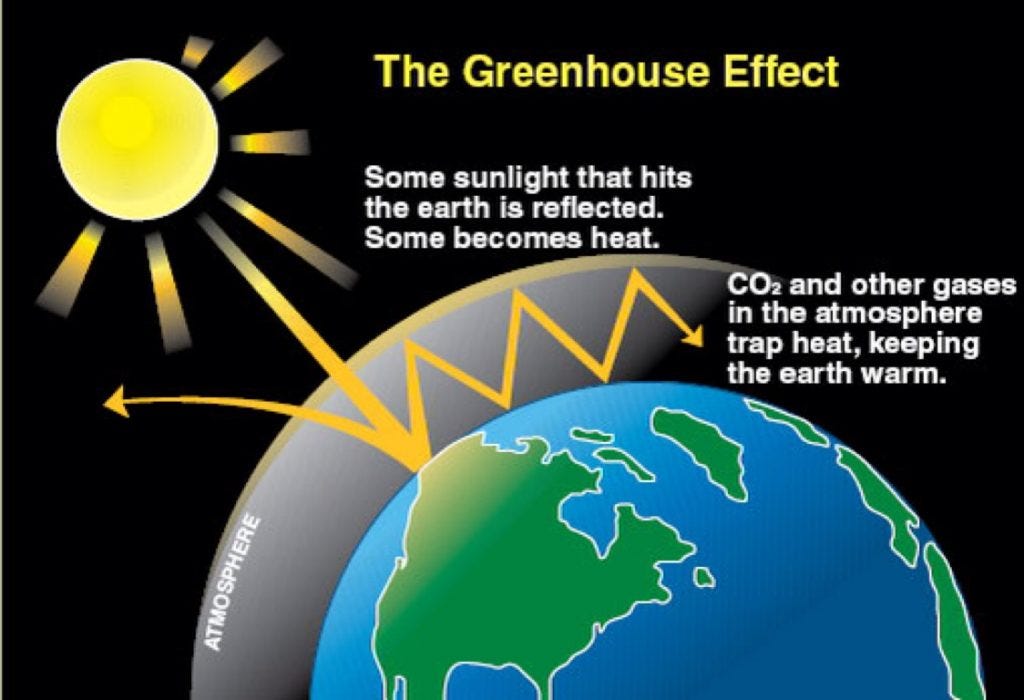



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium
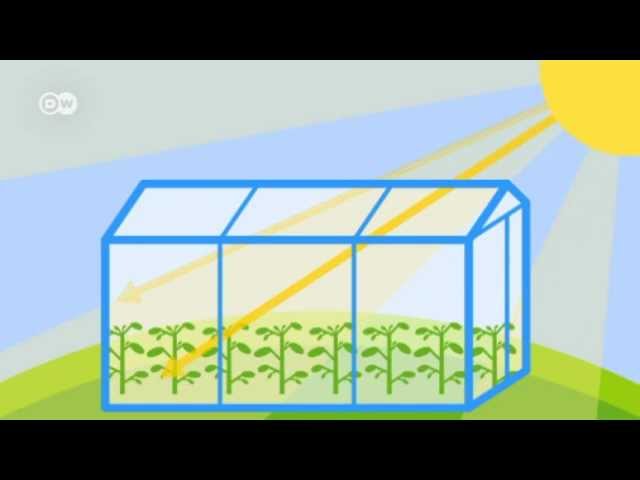



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas Youtube
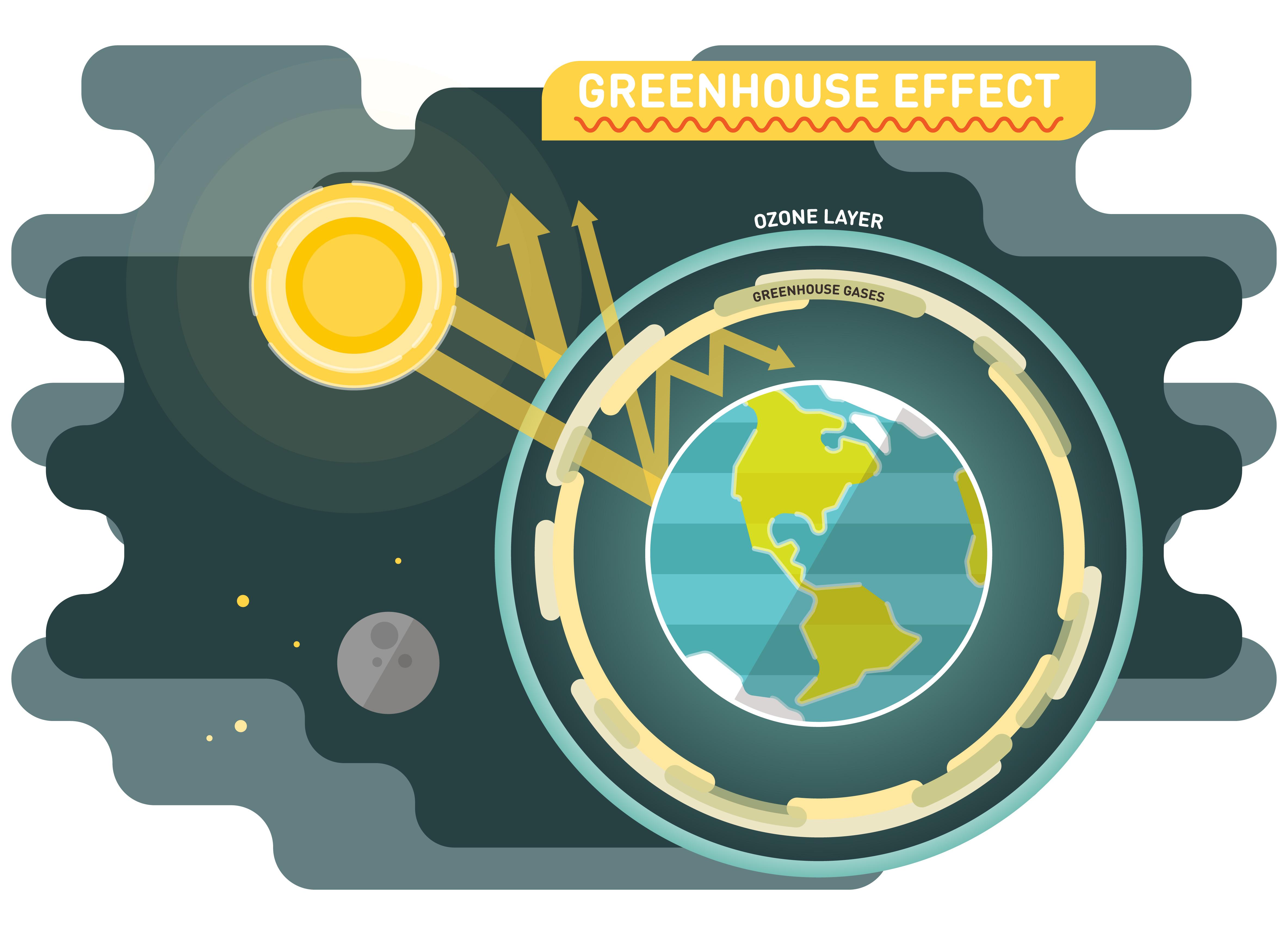



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate



What Is A Global Warming Potential And Which One Do I Use Ghg And Carbon Accounting Auditing Management Training Greenhouse Gas Management Institute




K1 Psx4w2wnatm




Carbon Dioxide Controls Earth S Temperature




Mean Machines Greenhouses Define The Terms 1 Greenhouse Gas A Gas That Contributes To The Greenhouse Effect By Absorbing Infrared Radiation Carbon Dioxide Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gases Tips To Reduce Your Greenhouse Gases Delmarfans Com
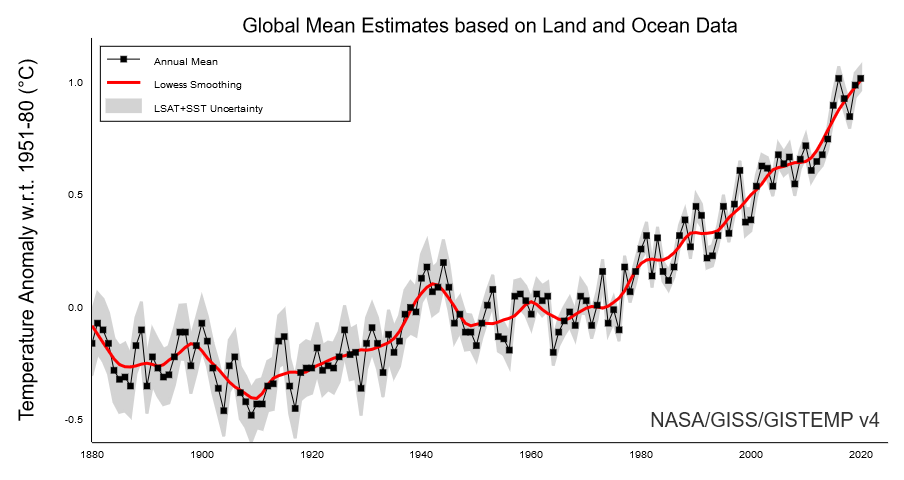



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect
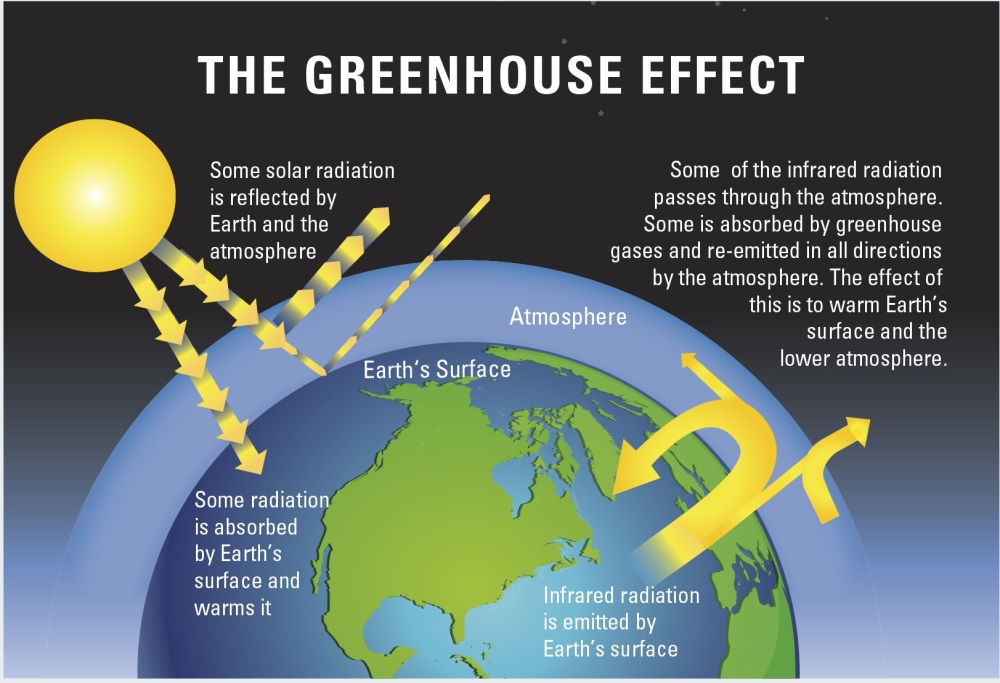



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases
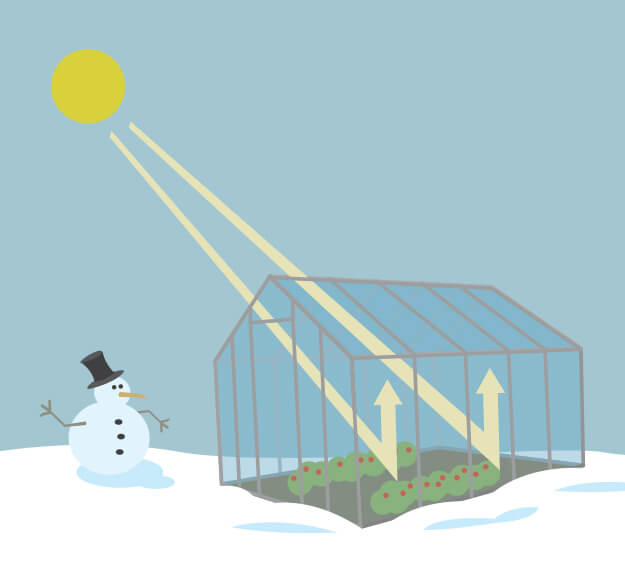




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




تل حقيقة سنوي What Is Greenhouse Effect In Short Hotelsanaasinn Com



What Does Greenhouse Gases Mean Definition Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Stands For Carbon Dioxide And Other Gaseous Emissions Resulting From Human Activity That Cause Heat To Be Trapped In




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
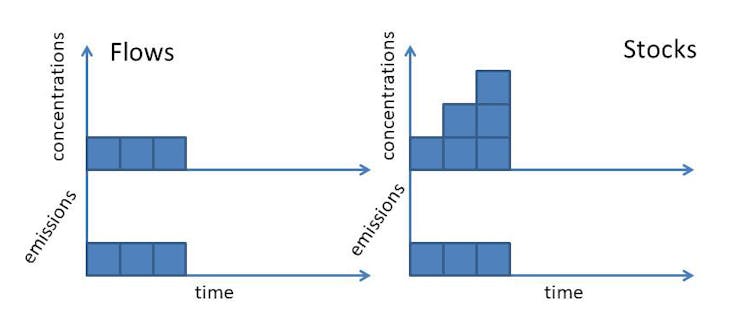



Why Methane Should Be Treated Differently Compared To Long Lived Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




Jargon Buster Science Based Targets




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay
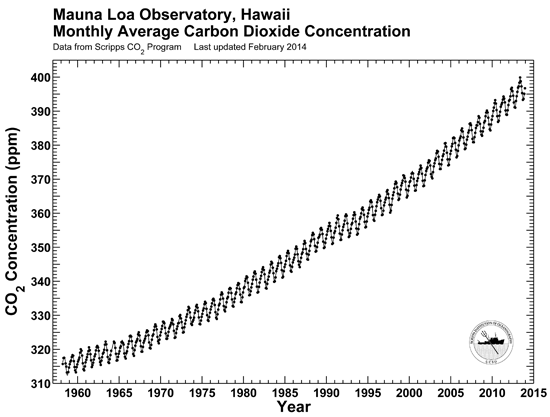



The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect



Environment For Kids Global Warming



3




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




What Are Greenhouse Gases How Are They Related To Global Warming



The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect
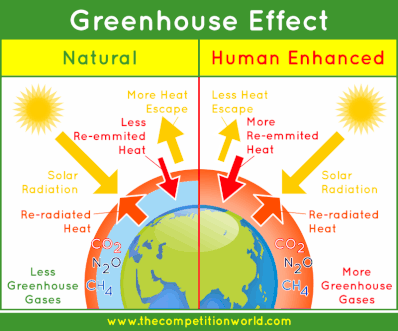



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Green House Effect Definition Meaning Video For Kids Youtube
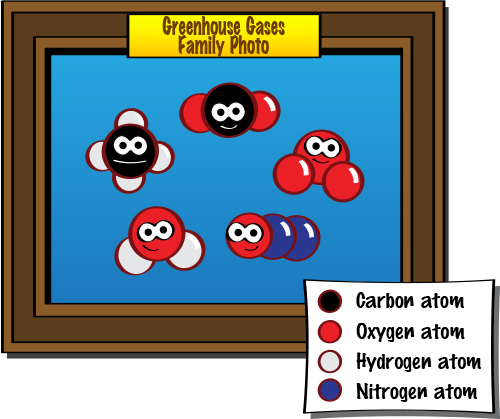



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids



Forests And Climate Change




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
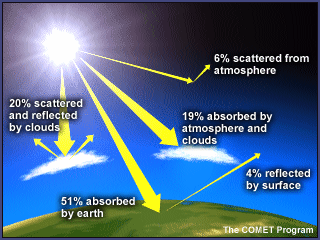



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
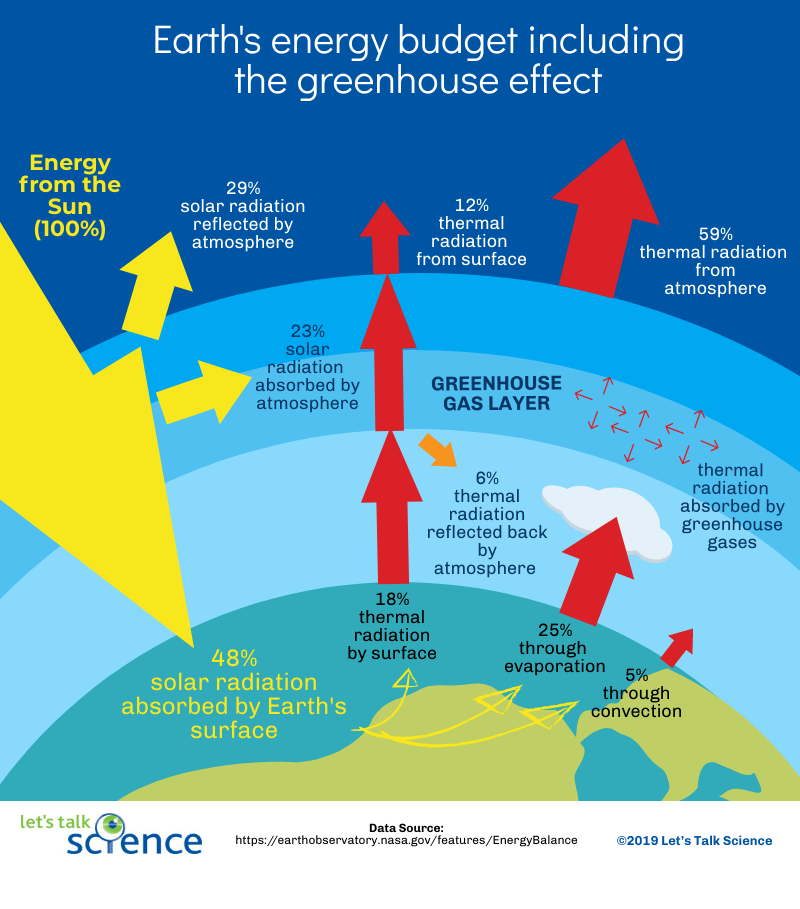



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science
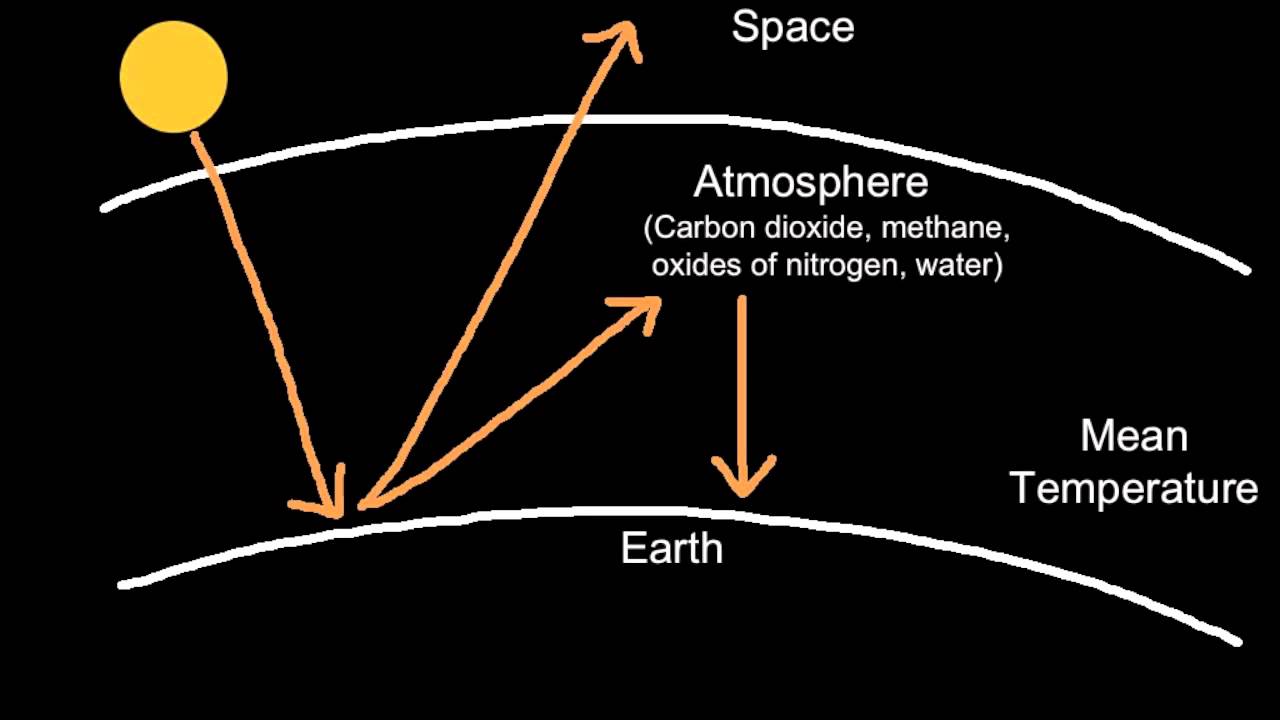



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Specific Interpretations Greenhouse Gases 101 Sustainability




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
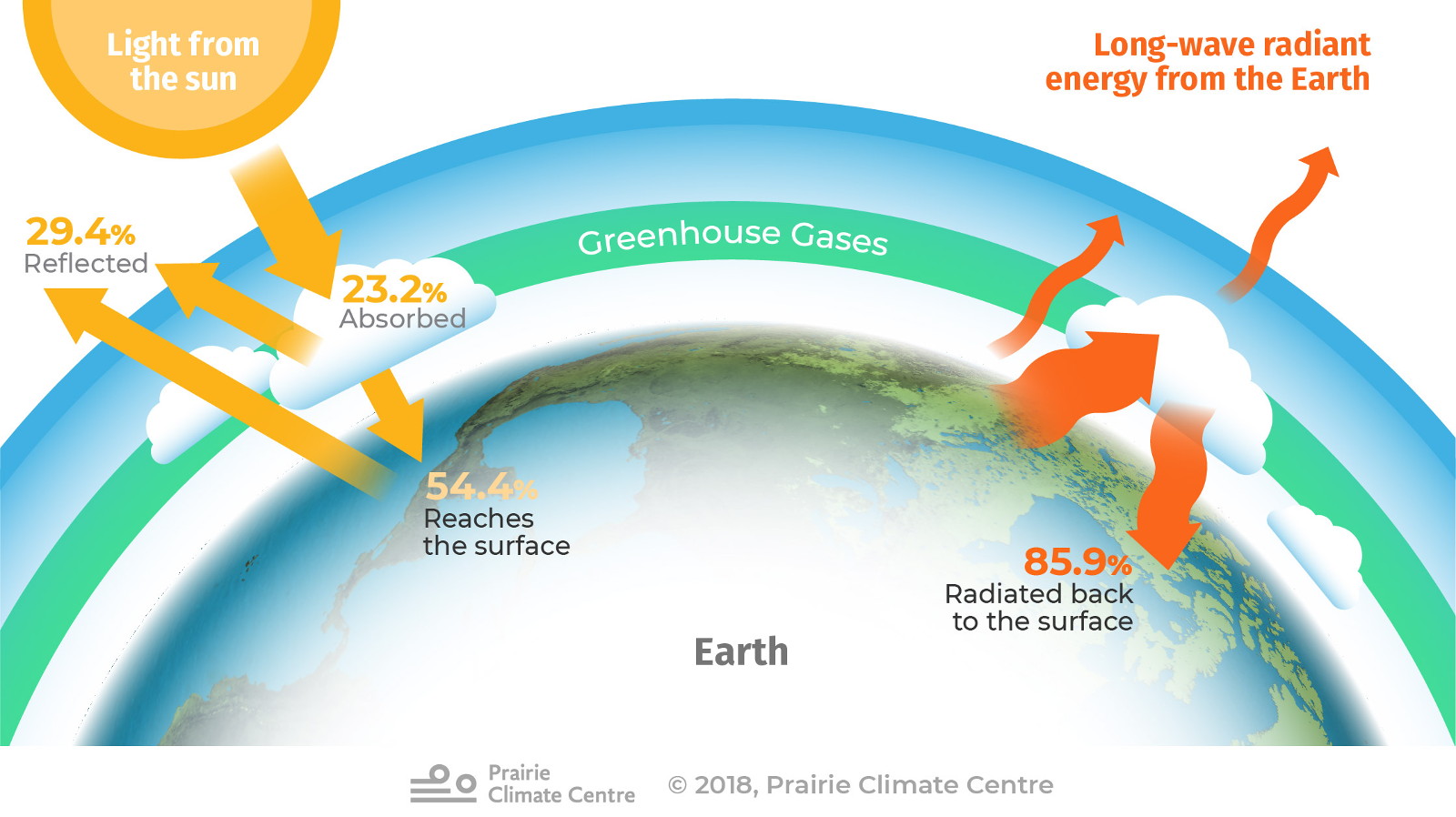



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
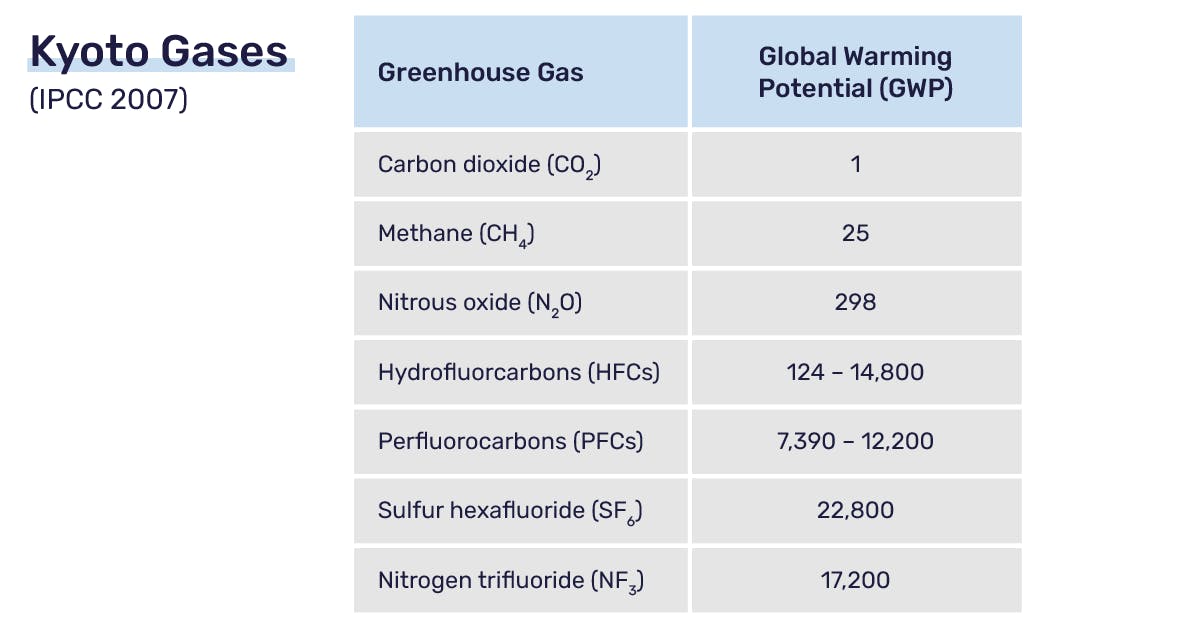



What Is Co2e And How Is It Calculated




What Is Climate Change Acciona Business As Unusual
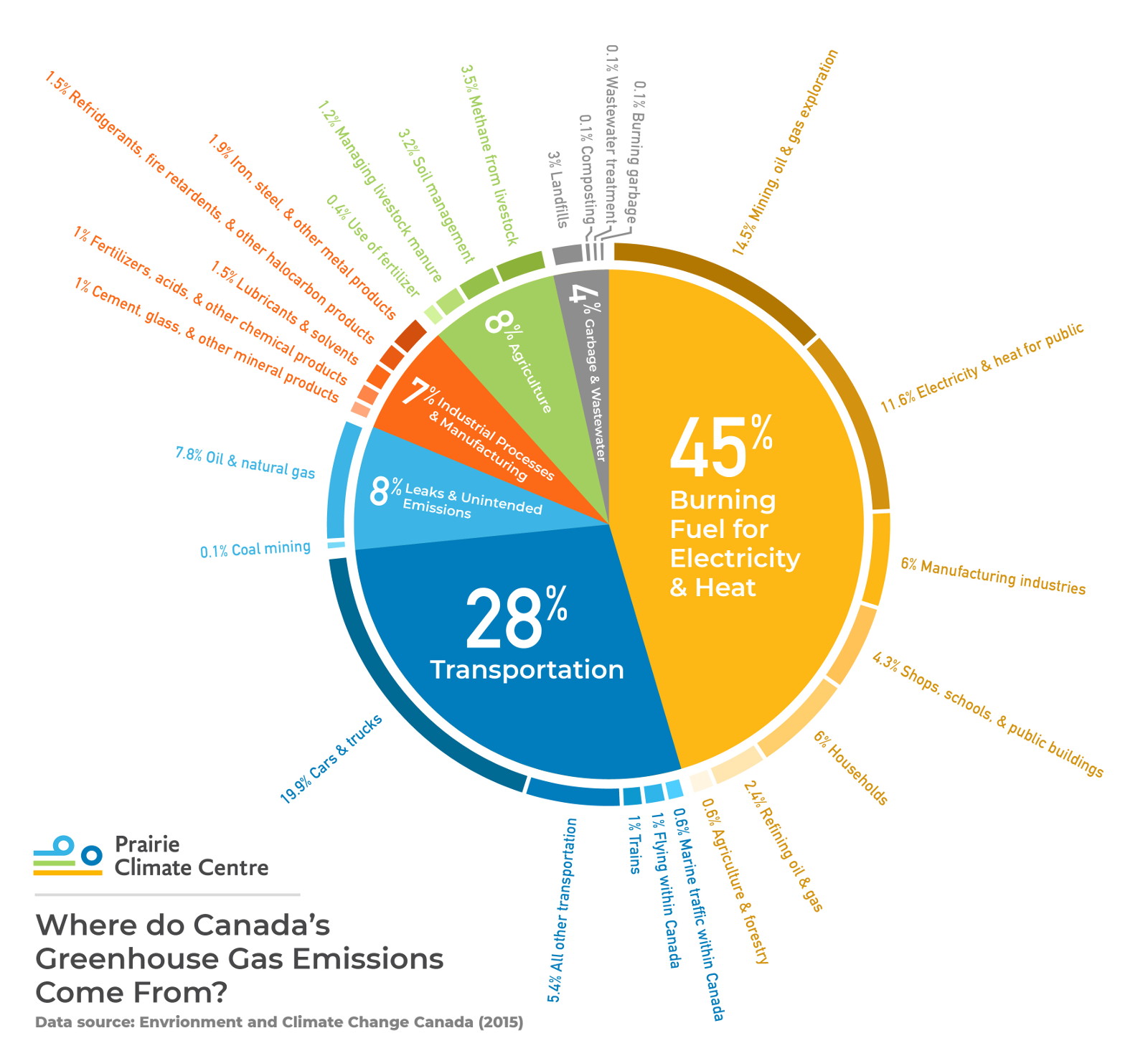



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




How To Stop Global Warming The 8 Best Solutions




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect E 3 Pages Definitions 2 Description 3 Greenhouse Gases 4 Greenhouse Gases Effect On Atmosphere Ppt Download




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
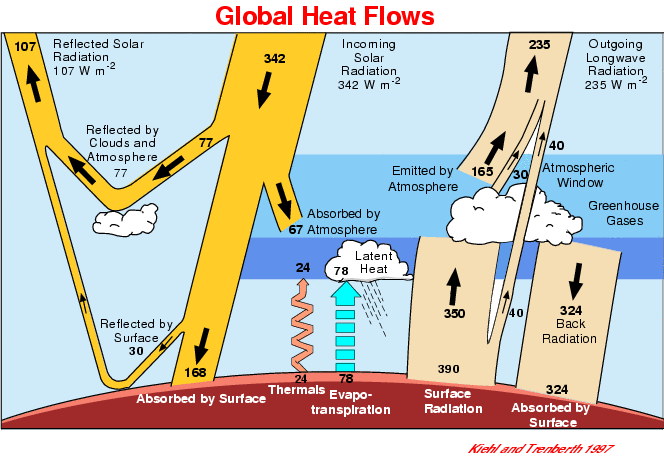



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿